Introduction
The world of software development is evolving at lightning speed, and artificial intelligence (AI) is taking center stage in this transformation. OpenAI has recently announced significant Codex upgrades, powered by GPT-5 Codex, designed to help developers become more productive, efficient, and creative.
From automated AI code review tools to seamless IDE integration, the upgraded Codex is no longer just a coding assistant — it’s maturing into a full-fledged engineering collaborator.
In this blog, we’ll dive deep into what the OpenAI Codex upgrades mean, explore their new features, and show how they’ll shape the future of coding and developer productivity with AI — with a special focus on Laravel workflows.
What is GPT-5 Codex?
At the heart of the new OpenAI Codex upgrades is GPT-5 Codex — a specialized version of OpenAI’s latest model fine-tuned for “agentic coding.”
Unlike earlier iterations that mostly supported interactive pair programming, GPT-5 Codex now goes much further. It can:
- Build entire projects from scratch
- Add and improve test coverage
- Debug and refactor large codebases
- Perform deep code reviews and catch critical issues
What makes GPT-5 Codex unique is its ability to adapt its reasoning depth depending on the task. For small fixes, it provides instant, lightweight solutions. For complex engineering challenges, it uses a more rigorous, step-by-step process that mirrors how senior developers think through problems.
What’s New: Key OpenAI Codex Upgrades
GPT-5 Codex Enhancements
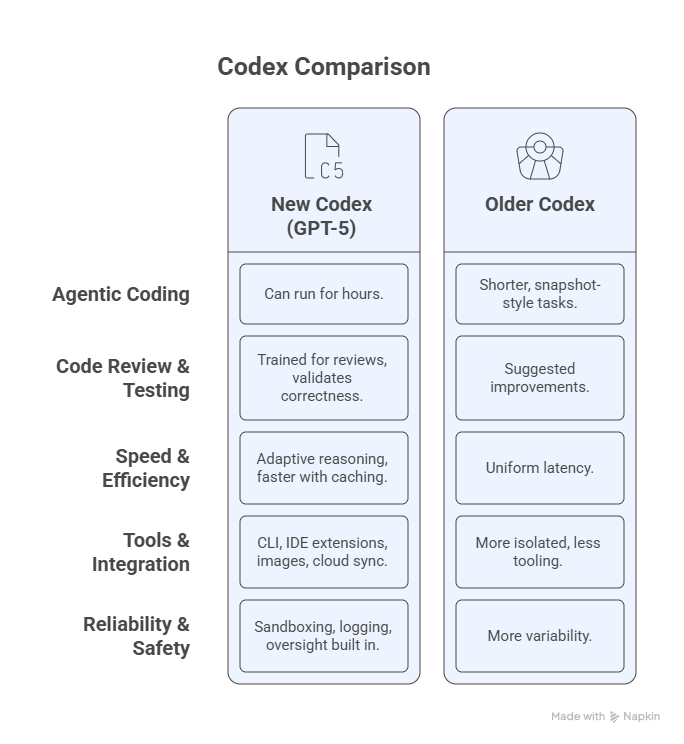
- Optimized for agentic coding — handling end-to-end tasks like building features, debugging, refactoring, testing, and reviews.
- Dynamically adjusts reasoning time: faster for simple issues, deeper for complex refactors.
- Trained specifically to catch bugs, navigate dependencies, and validate correctness with automated tests.
Better Tools & Integrations
Codex CLI
- Rebuilt around agentic coding workflows.
- Attach images (screenshots, wireframes, diagrams) to give coding context.
- Progress tracking with a to-do list.
- Clearer diffs and simplified approval modes.
IDE Extension
- Works in VS Code and other forks.
- Uses local editor context (open files, selections) for shorter, smarter prompts.
- Move tasks between cloud and local without losing context.
Codex Cloud
- ~90% faster on median completion times thanks to container caching.
- Automatic environment setup: scans for setup scripts, installs dependencies like
piporcomposer. - Handles images/screenshots even in the cloud for frontend/UI tasks.
AI Code Review Capabilities
- Automatic PR reviews on GitHub: when a draft PR becomes ready, Codex comments with feedback.
- Developers can explicitly invoke reviews (e.g.,
@codex review for security vulnerabilities). - Evaluations show Codex produces fewer, more important review comments — reducing noise and boosting trust.
Safety, Trust & Governance
- Sandboxed by default, with network access disabled unless explicitly allowed.
- Prompts developer approval for potentially risky commands.
- Provides logs, test results, and citations for human oversight.
- Categorized as “high capability” with safeguards in sensitive fields (e.g., biological/chemical).
Pricing & Availability
- Included in ChatGPT Plus, Pro, Business, Edu, Enterprise plans.
- Usage limits vary: casual sessions for Plus, intensive workloads for Pro/Enterprise.
- Shared credit pools available for teams.
- API key support for GPT-5 Codex is planned for CLI users.
What New Codex Adds vs Older Versions
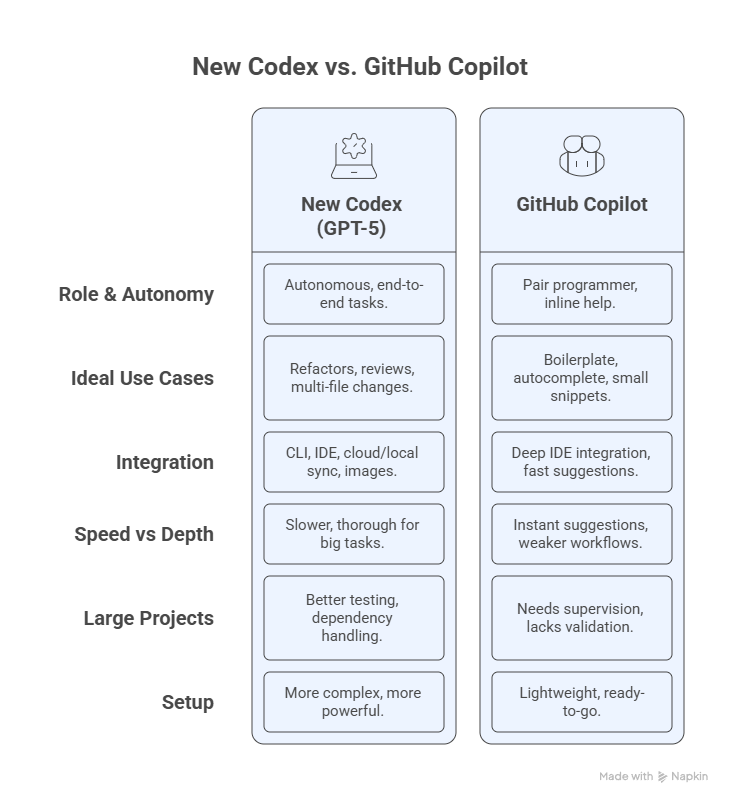
New Codex vs GitHub Copilot
Weaknesses of New Codex
Even with upgrades, challenges remain:
- Vague tasks still need careful prompting.
- Very large codebases may require human architectural oversight.
- Long tasks can be compute- and time-intensive.
- AI code review tools reduce errors but don’t eliminate the need for human review.
- Integration with legacy workflows may be non-trivial.
Codex (Upgraded GPT-5 Codex) for Laravel
Strengths
- Handles multi-file builds: controllers, models, migrations, routes, tests, services.
- AI code reviews catch Laravel-specific pitfalls (e.g., N+1 queries, missing validation, misused middleware).
- Generates strong Pest tests with mocks and DB coverage.
- Auto-detects
composer.jsonand runscomposer install. - Can scaffold Blade templates from wireframes/screenshots.
Trade-offs
- Slower for large refactors.
- May hallucinate around Laravel-specific service container or event/listener APIs.
- Sandbox/cloud needs explicit DB/API permissions.
Copilot for Laravel
Strengths
- Great for inline productivity:
- Controllers, routes, models, migrations.
- Boilerplate Eloquent queries.
- Blade snippets and loops.
- Instant suggestions while coding.
Limitations
- Weak in multi-file orchestration.
- No automated reviews — you catch N+1 queries yourself.
- Testing scaffolds are shallow.
Step-by-Step Workflow: Codex + Copilot in Laravel
(Keep your original 12-step detailed workflow here — it’s already excellent and long-form. Add minor keyword polish, e.g., “Codex upgrades” and “AI code review tools” in section headings where relevant.)
1) Project setup (one-time)
- Standards & tooling
composer require --dev pestphp/pest nunomaduro/larastan laravel/pint phpstan/phpstan friendsofphp/php-cs-fixerAdd scripts in composer.json:
{
"scripts": {
"test": "pest",
"lint": "pint",
"stan": "phpstan analyse --memory-limit=1G"
}
}
- Create
/phpstan.neonwith Laravel rules & level (start 5–6).
Copilot: enable in your IDE (VS Code / PhpStorm) for PHP/Blade.
Codex:
- Install the CLI/extension.
- Grant least-privilege repo access; allow running composer/npm & tests.
- Configure a “Laravel template” environment (PHP version, Node, database).
2) Write a tight task brief (for Codex)
Use a short, structured brief instead of a long chat:
Goal: Implement feature "Team Invitations".
Repo: <link> (Laravel 11, PHP 8.3, Pest, MySQL)
Constraints: Follow DDD-ish structure (Actions/DTOs), no Facades in domain layer.
Deliverables:
- Migration + Model: Invitation { email, token, team_id, expires_at, status }
- Controller + FormRequest + Policies
- Blade views: create form + list page
- Notification mail + queue
- Pest tests: model, controller, policy, feature flow
Quality gates:
- No N+1 (use eager loading)
- Validation/authorization on every write
- CSRF, mass assignment guarded
- Pass: composer test, lint, stan(level 6)
Runbook:
- If deps missing: composer install
- DB: sqlite :memory: in tests
Attach screenshots/wireframes if you have UI.
3) Let Codex scaffold the feature
Ask Codex to:
- Generate migrations, models, policies, requests, controllers, routes, views.
- Add factories/seeders.
- Create Pest tests for happy/edge paths.
- Run
pestand fix failing tests. - Produce a diff + TODO checklist.
Example CLI prompt:
Create the Team Invitations feature as per brief.
Explain design choices in NOTES.md.
Open a draft PR when tests pass.
4) Use Copilot for speed while iterating locally
Typical spots where Copilot shines:
- Eloquent scopes, small controller actions, Blade loops/components.
- Quick stubs for FormRequests/Policies.
- Converting ad-hoc queries to scopes:
public function scopePending(Builder $q): Builder {
return $q->where('status', 'pending');
}
5) Tests first mindset (Codex + Copilot)
- Ask Codex to generate failing Pest specs first; then implement.
- Good starting spec:
it('sends a signed invite and queues email', function () {
$team = Team::factory()->create();
$owner = User::factory()->for($team)->create();
actingAs($owner)
->post(route('invites.store'), ['email' => 'a@b.com'])
->assertRedirect();
expect(Invitation::first())->email->toBe('a@b.com');
Queue::assertPushed(SendInvitationMail::class);
});
Use Copilot to fill assertions & dataset variants quickly.
6) Database & seeding
- Migration example (Codex can write):
Schema::create('invitations', function (Blueprint $t) {
$t->id();
$t->foreignId('team_id')->constrained()->cascadeOnDelete();
$t->string('email')->index();
$t->string('token')->unique();
$t->timestamp('expires_at')->nullable()->index();
$t->string('status')->default('pending')->index();
$t->timestamps();
});
Factory to generate realistic data; seeder for local testing.
7) Blade/UI with screenshots
- Upload a wireframe screenshot to Codex and ask it to:
- Build Blade with Tailwind.
- Extract reusable Blade components (
<x-input>,<x-button>,<x-table>). - Generate cypress/playwright tests if you do E2E (optional).
8) Security & performance checklist (have Codex auto-review)
- Validation with
FormRequest - Authorization via Policy/Gate on every write
- Prevent mass assignment:
$fillable/ guarded patterns - Eager-load relations to avoid N+1
- Use
@csrf, signed routes for tokens - Don’t leak tokens in logs
- Queued mail/notifications, not sync
- Cache heavy reads (
Cache::remember()or query scopes + indexes)
Ask Codex:
“Review PR for security, auth, validation, N+1, and mass assignment. Suggest diffs only.”
9) Pull Request flow
- Draft PR (Codex can open it if configured).
- You push tweaks using Copilot.
- Codex review: ask it explicitly to review the PR against the checklist, and to propose minimal diffs.
- You accept/reject its patch set.
PR template (drop in .github/pull_request_template.md):
### What
- <summary>
### How
- <key design notes>
### Checklist
- [ ] Validation & Authorization in place
- [ ] No N+1 (show tinker or test evidence)
- [ ] Tests added/updated; `composer test` passes
- [ ] `composer lint` & `composer stan` pass
### Screenshots / Notes
10) CI you can copy (GitHub Actions)
.github/workflows/ci.yml
name: CI
on:
pull_request:
push:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
tests:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: shivammathur/setup-php@v2
with:
php-version: '8.3'
coverage: none
tools: composer
- run: composer install --prefer-dist --no-progress
- run: cp .env.example .env
- run: php artisan key:generate
- run: php artisan config:cache
- run: vendor/bin/pint --test
- run: vendor/bin/phpstan analyse --memory-limit=1G
- run: vendor/bin/pest
Ask Codex to keep CI green by pushing fixes if a step fails.
11) Release checklist
php artisan config:cache && route:cache && view:cache- Horizon/queues configured; mails/notifications are queued
- DB migrations tested on a staging clone
- Rollback plan (
migrate:rollback) & backups - Observability: Laravel Telescope (dev), Sentry/Bugsnag (prod)
12) Who does what (quick rule)
- Copilot: type faster (controllers, Blade, little queries, refactors you already know).
- Codex: create/reshape modules, write tests, chase bugs across files, run CI locally/in cloud, review PRs with a security/perf lens.
Why These OpenAI Codex Upgrades Matter
The combination of GPT-5 Codex and AI code review tools means developers now have a teammate that can:
- Spot issues earlier in the lifecycle.
- Automate repetitive scaffolding tasks.
- Scale testing across large Laravel apps.
- Improve developer productivity with AI by reducing time spent on boilerplate and debugging.
For teams, this translates to faster shipping cycles and higher-quality releases.
FAQs
Q: What are the key OpenAI Codex upgrades in 2025?
A: GPT-5 Codex, faster Codex Cloud, IDE/CLI integration, and built-in AI code review tools.
Q: How does GPT-5 Codex improve code reviews?
A: It’s explicitly trained to analyze PRs, find bugs, highlight performance/security risks, and provide concise, correct review comments.
Q: Are AI code review tools better than human reviews?
A: They complement, not replace, humans — catching repetitive issues while humans handle architecture, design, and domain-specific trade-offs.
Q: How can Codex boost developer productivity with AI?
A: By scaffolding features, generating tests, running reviews, and reducing manual overhead — leaving devs free to focus on creative and complex work.
Q: What’s the difference between GPT-5 Codex and GitHub Copilot?
A: Codex is more autonomous and suited for large, multi-file tasks. Copilot excels at inline code suggestions.
Q: Is Codex safe for enterprise Laravel apps?
A: Yes, with sandboxing and developer approval prompts. Teams should still enforce best practices, CI/CD pipelines, and human oversight.
Further Resources on OpenAI Codex
In this section, you’d include the two links:
Conclusion
The OpenAI Codex upgrades powered by GPT-5 Codex mark a major leap in how developers work. No longer just autocomplete helpers, these AI code review tools bring autonomy, accuracy, and safety into modern software workflows.
For Laravel teams — and developers everywhere — this means higher quality, faster delivery, and greater developer productivity with AI.
Now is the perfect time to start experimenting with the upgraded Codex:
- Use Copilot for inline speed.
- Use Codex for larger features, tests, and reviews.
- Let both work together to transform your engineering process.
The future of coding isn’t human vs AI — it’s human + AI. And with the new OpenAI Codex upgrades, that future is already here.
Comments