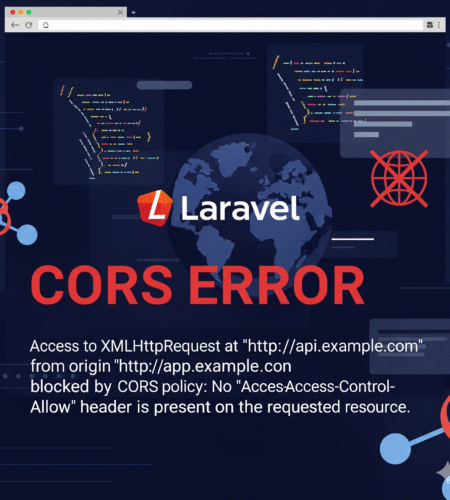
When working on modern web apps, it’s very common to keep frontend and backend separate. Maybe your React app runs at http://localhost:5173, and your Laravel API runs at http://localhost:8000. The first time you connect them, you may see this dreaded error:
Access to fetch at 'http://localhost:8000/api/user' from origin 'http://localhost:5173'
has been blocked by CORS policy: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present.
This is a Laravel CORS error, and it frustrates almost every beginner. Don’t worry — in this blog, we’ll go step by step, from what is CORS, how Laravel handles it, how to enable it in Laravel 11 and 12, common mistakes, and advanced tricks.
What is CORS?
CORS means Cross-Origin Resource Sharing. It’s a browser security rule that stops one website (origin) from directly requesting data from another website (different origin) unless the server explicitly allows it.
- Origin = scheme + host + port
Example:http://localhost:5173andhttp://localhost:8000→ different originshttps://api.example.comandhttps://example.com→ different origins
By default, browsers block such requests. The Laravel server must send special headers like:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://localhost:5173
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Authorization
Laravel and CORS Support
Older Laravel used barryvdh/laravel-cors package.
Now Laravel ships with fruitcake/laravel-cors middleware out of the box.
- Laravel 7 → first included
- Laravel 8, 9, 10 → stable
- Laravel 11 and upcoming Laravel 12 → still works the same
So if you see Laravel-cors Laravel 12 or laravel-cors Laravel 11 discussions, it simply means you just need to configure it correctly — no extra installation.
Step 1: Install (For Legacy Versions)
If you are using Laravel 6 or below, install manually:
composer require fruitcake/laravel-cors
php artisan vendor:publish --tag="cors"
For Laravel 7+, it’s already included.
Step 2: Laravel CORS Config
Check your file: config/cors.php
This file decides:
- Which paths need CORS headers (
paths) - Which origins are allowed (
allowed_origins) - Which HTTP methods are allowed (
allowed_methods) - Whether cookies (credentials) are supported (
supports_credentials)
Example: Development Setup
return [
'paths' => ['api/*', 'sanctum/csrf-cookie'],
'allowed_methods' => ['*'],
'allowed_origins' => [
'http://localhost:5173',
'http://127.0.0.1:5173'
],
'allowed_headers' => ['*'],
'supports_credentials' => true,
];
Example: Production API for a Single Domain
'paths' => ['api/*'],
'allowed_methods' => ['GET', 'POST', 'PUT', 'PATCH', 'DELETE'],
'allowed_origins' => ['https://myapp.com'],
'allowed_headers' => ['Content-Type', 'Authorization'],
'supports_credentials' => true,
Example: Laravel CORS Allow All (Testing Only)
'paths' => ['*'],
'allowed_methods' => ['*'],
'allowed_origins' => ['*'],
'allowed_headers' => ['*'],
'supports_credentials' => false,
Warning: Never use '*' in production if you need cookies or security.
Step 3: Middleware
Laravel automatically registers Laravel-CORS middleware in app/Http/Kernel.php:
\Fruitcake\Cors\HandleCors::class,
Check it exists in $middleware. If not, add it manually.
Step 4: Clear Cache
Sometimes old config causes confusion. Run:
php artisan config:clear
php artisan cache:clear
Common Laravel-CORS Errors and Fixes
1. Error:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin missing
- Ensure middleware is active.
- Ensure your path matches API routes (like
api/*).
2. Error:
The value of the 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header must not be '*' when credentials flag is true
- Fix: If
supports_credentials = true, you must specify exact origins (likehttp://localhost:5173).
3. Error: Preflight request (OPTIONS) fails
- Fix: Add
OPTIONSmethod inallowed_methods. - Make sure Nginx/Apache does not block
OPTIONS.
4. Laravel CORS not working in Laravel 11 or Laravel 12
- Fix: Check
cors.phpconfig is published. - Don’t install
barryvdh/laravel-corsagain — it’s already included.
How to Enable CORS in Laravel 11 (Step-by-Step)
- Check
config/cors.phpexists. - Add your frontend domain in
allowed_origins. Example:
'allowed_origins' => ['http://localhost:5173', 'https://myfrontend.com'],
3. Add \Fruitcake\Cors\HandleCors::class, middleware if missing.
4. Clear config cache:
php artisan config:clear
- Test with
curl -ior frontend request.
That’s all. Now your Laravel 11 CORS setup works.
Advanced: Laravel CORS with Sanctum
If you use Laravel Sanctum for SPA authentication:
- Set in
.env:
SESSION_DOMAIN=.myapp.com
SANCTUM_STATEFUL_DOMAINS=frontend.myapp.com,localhost:5173
2. In cors.php:
'paths' => ['api/*', 'sanctum/csrf-cookie'],
'supports_credentials' => true,
3. Frontend Axios request must include withCredentials: true.
Debugging Tips
- Use browser DevTools → Network tab → Check Response Headers
You should see:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://localhost:5173
- If not present, your middleware/config is not applied.
- For API gateways (Nginx, Apache, Cloudflare), ensure they don’t strip CORS headers.
Conclusion
- Laravel CORS is essential for any frontend-backend project.
- Use Laravel CORS config (
config/cors.php) to allow origins, methods, and headers. - Use
Laravel CORS allow allonly for local testing. - In Laravel 11 and Laravel 12, you don’t need to install extra packages — it’s built-in.
- Always double-check middleware and clear caches when debugging.
By following these steps, you’ll never be stuck with a Laravel-cors error again
Comments