Introduction
Timezone management is one of the most important yet overlooked aspects of application development, especially for global applications. Laravel, being a robust PHP framework, offers various tools and methods to handle timezone-related issues effectively. However, when the time zone is not configured correctly, it can lead to incorrect timestamps, wrong time zone conversions, and inconsistencies in data representation. In this blog, we will address common Laravel timezone issues and provide detailed solutions, including the use of the Laravel-timezone package, setting the timezone correctly, and solving common timezone-related issues in PHP.
By the end of this blog, you will have a clear understanding of how to tackle Laravel timezone issues, ensure accurate time handling, and avoid mistakes in your applications.
Common Timezone Issues in Laravel
Timezone issues typically arise when the timezone is not set properly either in the application’s configuration or the underlying database. These issues can be resolved by configuring the timezone in multiple places, including the Laravel timezone package, environment files, and database configurations.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the common problems and their solutions.
1. Setting Timezone in Laravel
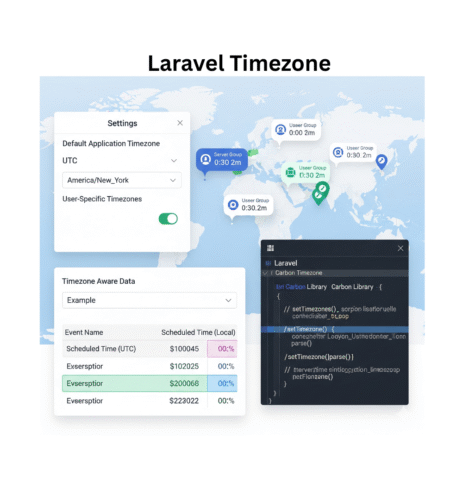
Setting the correct timezone in Laravel is crucial for managing time-related operations. By default, Laravel uses UTC for storing dates and times in the database, which is a great approach for applications that operate across multiple time zones. However, if you need to display dates in the user’s local timezone, you need to ensure the Laravel timezone is set properly.
How to set the timezone:
- Open
config/app.phpin your Laravel project. - Find the
'timezone'key and set it to your desired timezone. For example:
'timezone' => 'UTC', // Or any other timezone like 'America/New_York', 'Europe/London', etc.
You can also use dynamic timezone settings by leveraging env variables. This allows you to change the timezone without modifying the codebase.
'timezone' => env('APP_TIMEZONE', 'UTC'), // Reads from the environment fileThis way, you can dynamically set the timezone using the .env file:
APP_TIMEZONE=America/New_YorkThis will allow you to easily switch timezones across different environments (e.g., development, production).
2. Laravel-Timezone Package
The Laravel-timezone package is a great tool to manage and set timezones in your Laravel applications more efficiently. This package simplifies timezone handling, especially when dealing with user preferences or time-related data.
How to install and use the Laravel-timezone package:
To install the Laravel-timezone package, run the following composer command:
composer require joeybaker/laravel-timezoneOnce installed, you can use this package to handle timezones in your application easily. It provides various features like handling timezone offsets, converting between timezones, and storing user timezone preferences.
For example, to convert a timestamp to the user’s timezone:
use JoeyBaker\Timezone\Timezone;
// Convert a given timestamp to a specific timezone
$date = Carbon::parse('2025-09-17 10:00:00');
$timezone = 'America/New_York';
$convertedDate = Timezone::convert($date, $timezone);
echo $convertedDate; // This will output the date in New York time
This simplifies the process of managing timezones in your application without manually handling Carbon or PHP date functions.
3. Laravel Timezone Issue: PHP and Database Mismatches
Timezone issues often arise when the application timezone doesn’t match the timezone of the database or PHP configurations. A mismatch can lead to incorrect timestamps being saved in the database or displayed on the front end.
Example Problem:
Let’s say a customer from New York places an order on September 17, 2025 at 10:00 AM New York time, but the order timestamp is saved as 2025-09-17 02:00:00 UTC in the database, which may cause confusion when retrieved.
Cause: The default timezone setting in Laravel is UTC and the database timezone is also not consistent with it.
Solution:
- Set database timezone to UTC to avoid discrepancies: For MySQL, ensure that the timezone is set to UTC in
config/database.php:
'mysql' => [
'driver' => 'mysql',
'host' => env('DB_HOST', '127.0.0.1'),
'port' => env('DB_PORT', '3306'),
'database' => env('DB_DATABASE', 'forge'),
'username' => env('DB_USERNAME', 'forge'),
'password' => env('DB_PASSWORD', ''),
'charset' => 'utf8mb4',
'collation' => 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci',
'timezone' => '+00:00', // UTC time for consistency
],
By setting both the application timezone and database timezone to UTC, you can store timestamps consistently across regions.
Convert stored UTC timestamps to the local timezone when displaying them:
$order = Order::find($orderId);
$localTime = $order->created_at->setTimezone('America/New_York');
echo $localTime->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');
- This ensures the correct local time is displayed for each user, regardless of where they are located.
4. Handling Daylight Saving Time (DST)
Daylight Saving Time (DST) can cause confusion when dealing with timezones, especially in regions like New York, which shifts between Standard Time and Daylight Time. If you don’t handle DST transitions properly, it could lead to one-hour discrepancies in timestamps.
Solution:
When dealing with timezones affected by DST, always use timezone names (e.g., America/New_York) instead of fixed offsets (-05:00), as Carbon and Laravel automatically adjust for DST.
$date = Carbon::parse('2025-03-15 01:00:00')->setTimezone('America/New_York');
This will automatically adjust the time for DST, ensuring correct time conversion.
5. Laravel Timezone Issue with PHP’s date() Function
If you’re using PHP’s native date() function, you might encounter timezone issues since the default PHP timezone might not be configured to match Laravel’s timezone.
Solution:
To ensure consistent timezone handling, set the default timezone in PHP by modifying your php.ini file:
date.timezone = "UTC"Alternatively, you can set the timezone programmatically in your Laravel project:
date_default_timezone_set('UTC');
This ensures that PHP’s date functions respect the timezone set by Laravel.
Case Study: Timezone Issues in ShopNow E-Commerce Platform
Background:
ShopNow is a global e-commerce platform serving customers in multiple regions, including North America, Europe, and Asia. The platform is built with Laravel, but they faced several timezone-related issues that created confusion for users when checking timestamps for their orders, shipments, and reviews.
1. Incorrect Timezone Display for Orders
Scenario:
A customer in New York places an order at 10:00 AM on September 17, 2025. However, when they check the status of their order on ShopNow, they see the order timestamp displayed as 2025-09-17 02:00:00 UTC, which is 6 hours off from their local time.
Cause:
The application’s timezone was set to UTC, but it wasn’t converting the time to the user’s local timezone when displaying it. This discrepancy between the stored UTC timestamp and the displayed local time led to confusion for the user.
Solution:
ShopNow fixed this issue by ensuring all timestamps were stored in UTC, which is best practice for global applications. They then used Carbon to convert the timestamps to the customer’s local timezone before displaying the data:
$order = Order::find($orderId);
$localTime = $order->created_at->setTimezone('America/New_York');
echo $localTime->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');
By implementing this change, the platform displayed the correct order time in the user’s local timezone, ensuring accurate and consistent time displays for customers across different regions.
2. Timezone Mismatch Between Database and Application
Scenario:
ShopNow stored order dates in a MySQL timestamp column. When a customer in New York placed an order at 10:00 AM New York time, it was saved as 2025-09-17 14:00:00 UTC in the database. However, when the customer viewed their order, the timestamp appeared as 2025-09-17 06:00:00, causing confusion about the actual order time.
Cause:
The database timezone was not consistent with the application timezone. While the application was set to UTC, the database had different settings, leading to discrepancies when retrieving and displaying data.
Solution:
To resolve this, ShopNow standardized both the database and application timezones to UTC. They also ensured that when fetching timestamps from the database, the times were converted to the customer’s local timezone for accurate display.
'mysql' => [
'timezone' => '+00:00', // Use UTC for consistency
],
When displaying the timestamp, they used Carbon to convert the time to the customer’s local timezone, ensuring that the order timestamp was shown correctly for all users.
3. Daylight Saving Time (DST) Confusion
Scenario:
A customer in New York placed an order at 1:00 AM on March 15, 2025, during the DST transition. However, when the order timestamp was retrieved, it was shifted by one hour, causing confusion about whether the time was during the DST switch.
Cause:
The application did not account for the DST transition when handling timestamps, and the time zone conversion did not adjust for daylight savings.
Solution:
ShopNow addressed this by ensuring the use of timezone names (e.g., America/New_York) in the application. By using timezone names, Carbon and Laravel automatically adjusted for Daylight Saving Time when displaying timestamps:
$date = Carbon::parse('2025-03-15 01:00:00')->setTimezone('America/New_York');
This ensured that timestamps were correctly adjusted during the DST transition, preventing any confusion for users in affected regions.
4. Incorrect Timezone Handling for API Responses
Scenario:
ShopNow integrated with an external payment provider that returned transaction timestamps in UTC. However, when displaying the transaction date on the user’s profile, the application didn’t adjust the UTC time to the user’s local timezone, leading to incorrect display.
Cause:
The external API provided transaction timestamps in UTC, but the platform didn’t convert them to the customer’s local timezone when displaying the data.
Solution:
To fix this, ShopNow used Carbon to adjust the timestamp to the user’s timezone before displaying it:
$apiTransactionDate = Carbon::parse($apiResponse['transaction_date']);
$localTransactionDate = $apiTransactionDate->setTimezone('America/New_York');
echo $localTransactionDate->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');
This ensured that all timestamps returned from external APIs were displayed in the user’s local timezone, offering a consistent and accurate experience across the platform.
5. Inconsistent Timezone Configuration in Cron Jobs
Scenario:
ShopNow scheduled email notifications to be sent once an order had shipped. However, users in different timezones were receiving these notifications at incorrect times, due to the cron job running based on the server’s system time.
Cause:
The cron job was not accounting for the user’s local timezone and was relying on the server’s default timezone, which caused notifications to be sent at the wrong time.
Solution:
ShopNow fixed this by ensuring that the cron jobs ran at the correct time according to the customer’s timezone. They used Laravel’s built-in scheduler and set the correct timezone for each task:
$schedule->call(function () {
// Logic to send notification emails
})->timezone('America/New_York')->dailyAt('10:00');
This change ensured that notifications were sent at the correct local time, regardless of where the user was located.
By addressing these timezone-related issues, ShopNow was able to enhance the user experience and ensure that time-related data was consistent and accurate across the platform. These solutions helped them overcome timezone discrepancies and maintain a smooth operation for their global user base.
Bonus: Laravel Change Timezone Dynamically
In some applications, users may be located across different timezones, and their timezone preferences need to be handled dynamically. Laravel change timezone dynamically allows you to customize and adjust the application’s timezone based on the user’s preferences or location.
This functionality is particularly useful in applications like e-commerce platforms, social networks, or global services, where users from different regions interact with the platform at different times.
How to Dynamically Change Timezone in Laravel
- Using User Preferences:
The first method to change the timezone dynamically is to allow users to select their timezone and store it in the database. This way, you can use the user’s stored timezone to display time correctly based on their location. Step-by-step Process:- Store the user’s timezone preference in the database, typically in the
userstable.
- Store the user’s timezone preference in the database, typically in the
// Add a column to the users table for storing the timezone
Schema::table('users', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->string('timezone', 50)->default('UTC');
});
- Allow the user to select their timezone from a dropdown (e.g.,
America/New_York,Europe/London) when they register or update their profile. - In your controller, fetch the user’s stored timezone and set it dynamically for that session:
// Controller method to set the timezone
public function setTimezone(Request $request)
{
$timezone = $request->user()->timezone; // Fetch timezone from the database
config(['app.timezone' => $timezone]); // Set the application's timezone
date_default_timezone_set($timezone); // Adjust the PHP timezone
}
- Now, when the user visits your application, it will use their chosen timezone, and any time displayed will be adjusted according to their selection.
Automatically Setting Timezone Based on Location:
If you want to automatically set the timezone based on the user’s geographic location (e.g., through their IP address), you can use a service like GeoIP to determine the user’s location and then adjust the timezone accordingly.
Example using a third-party package:
Install a package that can fetch the user’s location (e.g., geoip2/geoip2):
composer require geoip2/geoip2
In your controller or middleware, use the location data to set the timezone dynamically.
use GeoIp2\Database\Reader;
$reader = new Reader('/path/to/GeoLite2-City.mmdb');
$record = $reader->city($request->ip());
$timezone = $record->location->timeZone;
config(['app.timezone' => $timezone]); // Dynamically set timezone
date_default_timezone_set($timezone); // Adjust PHP's timezone
Setting Timezone Based on Session or Request:
Another way to handle dynamic timezone changes is by using sessions or request data to set the timezone for the duration of a user’s session.
Example using session:
public function setSessionTimezone(Request $request)
{
// Assume the user has selected a timezone from a dropdown
session(['timezone' => $request->timezone]);
config(['app.timezone' => $request->timezone]); // Set timezone for the app
date_default_timezone_set($request->timezone); // Adjust PHP's timezone
}
With this approach, the timezone is set dynamically per session and ensures that each user sees the correct time based on their preferences or location.
Conclusion
Timezone management in Laravel is an essential aspect of building global applications, ensuring that users from various time zones experience accurate and consistent time-related data. By setting the right timezone in Laravel’s configuration, leveraging powerful tools like the Laravel-timezone package, and implementing dynamic timezone changes, you can enhance the user experience across different regions.
Understanding and resolving timezone issues early in the development process can prevent confusion, ensure correct data presentation, and improve the overall functionality of your application. Whether you’re storing dates in UTC or dynamically adjusting them based on user preferences, Laravel provides you with all the necessary tools to handle time effectively.
By following the solutions discussed in this blog, you can avoid common pitfalls such as incorrect time displays, mismatched database timezones, and issues related to Daylight Saving Time (DST). With the proper timezone configuration, you can ensure your application runs smoothly and delivers a seamless experience to users worldwide.
Resources
Here are some important resources to help you better understand and manage timezones in Laravel:
Comments