Abstract
This blog post delves into the exciting realm of building a real-time, browser-based voice assistant powered by OpenAI’s cutting-edge APIs. We’ll explore how to leverage WebRTC for efficient audio streaming from the browser, connect it to a Flask backend, and integrate with OpenAI’s audio transcription (Whisper), real-time text-to-speech (TTS), and chat completion (GPT) services to create an interactive, low-latency conversational experience. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the architecture, key technologies, and code necessary to implement your own AI voice assistant.
1. Introduction: The Dawn of Real-Time AI Conversations
- The Evolution of Voice Assistants: From rule-based systems to today’s AI-driven conversational agents.
- The Promise of Real-Time Interaction: Why low latency is crucial for natural conversations.
- OpenAI’s Role: How their recent API advancements (streaming, new TTS models) make this achievable.
- What We’ll Build: A browser-based voice assistant that listens, transcribes, processes with GPT, and speaks back, all in near real-time.
- Key Technologies: WebRTC, WebSockets, Flask, OpenAI APIs (Whisper, GPT, TTS).
2. Architectural Overview: The Pieces of the Puzzle
Visualizing the system helps understand the data flow.
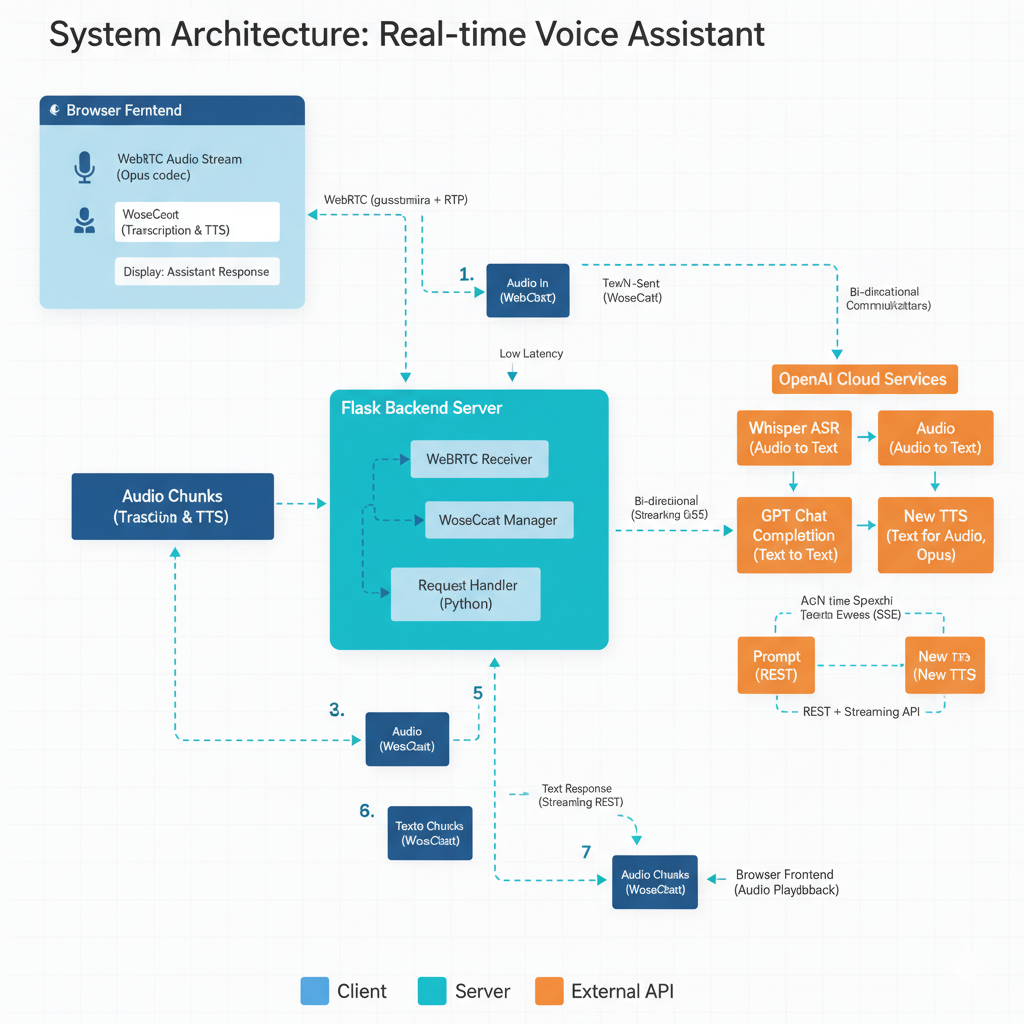
- Browser Frontend:
- Captures audio via
getUserMediaand WebRTC. - Sends audio chunks to the backend.
- Receives and plays back streamed audio from the backend.
- Displays transcribed text and AI responses.
- Captures audio via
- Flask Backend Server:
- Receives WebRTC audio streams.
- Acts as an orchestrator for OpenAI API calls.
- Handles WebSockets for bi-directional communication with the frontend.
- Manages the state of the conversation.
- OpenAI Cloud Services:
- Whisper API (ASR – Automatic Speech Recognition): Transcribes user’s spoken audio into text.
- Chat Completions API (GPT): Processes text, understands intent, and generates intelligent responses.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) API: Converts AI’s text response into natural-sounding speech.
3. Frontend: Capturing and Playing Audio with WebRTC and WebSockets
This section will focus on the client-side JavaScript.
3.1 Getting User Media and Sending Audio
getUserMedia: How to request microphone access.- WebRTC (
RTCPeerConnection):- Setting up peer connections.
- Adding audio tracks.
RTCDatachannel(Optional, for control messages, though WebSockets are more common for this).- Important: For simpler audio streaming to a server (not peer-to-peer), we often use
MediaRecorderwith WebSockets or stream raw audio bytes. However, WebRTC can be configured to send to a backend server as a “peer.” We will focus onMediaRecorder+ WebSockets for clarity and common practice in this context, as it’s often simpler for client-to-server audio. If WebRTC is a strict requirement for the audio transport, the complexity increases significantly for server-side handling (e.g.,aiortcin Python). Let’s stick toMediaRecorderand WebSockets for audio transport, as it’s more direct for streaming to an HTTP server.
MediaRecorderand WebSockets:- Recording audio chunks.
- Sending
Blobobjects or converting to base64 for WebSocket transmission. - Handling
ondataavailableevents.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Real-Time Voice Assistant</title>
<style>
body { font-family: sans-serif; display: flex; flex-direction: column; align-items: center; margin-top: 50px; }
button { padding: 10px 20px; font-size: 1.2em; cursor: pointer; }
#messages { width: 80%; max-width: 600px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid #ccc; overflow-y: scroll; padding: 10px; margin-top: 20px; }
.user-message { color: blue; }
.assistant-message { color: green; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>AI Voice Assistant</h1>
<button id="startButton">Start Assistant</button>
<button id="stopButton" disabled>Stop Assistant</button>
<div id="messages"></div>
<script>
const startButton = document.getElementById('startButton');
const stopButton = document.getElementById('stopButton');
const messagesDiv = document.getElementById('messages');
let mediaRecorder;
let ws;
let audioContext;
let audioQueue = [];
let isPlaying = false;
async function initAudioContext() {
if (!audioContext) {
audioContext = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)();
}
}
async function startRecording() {
startButton.disabled = true;
stopButton.disabled = false;
messagesDiv.innerHTML = '';
appendMessage('Assistant: Initializing...', 'assistant-message');
await initAudioContext();
try {
const stream = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({ audio: true });
mediaRecorder = new MediaRecorder(stream, { mimeType: 'audio/webm; codecs=opus' }); // opus is efficient
ws = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:5000/ws');
ws.onopen = () => {
appendMessage('Assistant: Connected to server. Speak now!', 'assistant-message');
mediaRecorder.start(1000); // Send data every second
};
ws.onmessage = async (event) => {
const data = JSON.parse(event.data);
if (data.type === 'transcription') {
appendMessage(`You: ${data.text}`, 'user-message');
} else if (data.type === 'response_text') {
appendMessage(`Assistant: ${data.text}`, 'assistant-message');
} else if (data.type === 'audio_chunk') {
// Decode base64 audio and add to queue
const audioData = Uint8Array.from(atob(data.audio_base64), c => c.charCodeAt(0)).buffer;
audioQueue.push(audioData);
if (!isPlaying) {
playNextAudioChunk();
}
}
};
ws.onclose = () => {
appendMessage('Assistant: Disconnected from server.', 'assistant-message');
stopRecording();
};
ws.onerror = (error) => {
console.error('WebSocket Error:', error);
appendMessage('Assistant: WebSocket error occurred.', 'assistant-message');
stopRecording();
};
mediaRecorder.ondataavailable = (event) => {
if (event.data.size > 0 && ws && ws.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) {
// Convert Blob to ArrayBuffer and then to base64 for WebSocket
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = () => {
const base64Audio = btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new Uint8Array(reader.result)));
ws.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'audio', audio_base64: base64Audio }));
};
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(event.data);
}
};
mediaRecorder.onstop = () => {
stream.getTracks().forEach(track => track.stop());
};
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error accessing microphone:', err);
appendMessage('Assistant: Error accessing microphone. Please allow access.', 'assistant-message');
stopRecording();
}
}
function stopRecording() {
startButton.disabled = false;
stopButton.disabled = true;
if (mediaRecorder && mediaRecorder.state !== 'inactive') {
mediaRecorder.stop();
}
if (ws) {
ws.close();
}
// Clear audio queue and stop playback
audioQueue = [];
isPlaying = false;
}
async function playNextAudioChunk() {
if (audioQueue.length > 0 && !isPlaying) {
isPlaying = true;
const audioData = audioQueue.shift();
try {
const audioBuffer = await audioContext.decodeAudioData(audioData);
const source = audioContext.createBufferSource();
source.buffer = audioBuffer;
source.connect(audioContext.destination);
source.onended = () => {
isPlaying = false;
playNextAudioChunk(); // Play next chunk when current one finishes
};
source.start(0);
} catch (e) {
console.error("Error decoding audio data", e);
isPlaying = false; // Reset to try playing next
playNextAudioChunk();
}
}
}
function appendMessage(text, className) {
const p = document.createElement('p');
p.textContent = text;
p.className = className;
messagesDiv.appendChild(p);
messagesDiv.scrollTop = messagesDiv.scrollHeight; // Auto-scroll
}
startButton.addEventListener('click', startRecording);
stopButton.addEventListener('click', stopRecording);
</script>
</body>
</html>3.2 Receiving and Playing Streamed Audio
- Web Audio API (
AudioContext,decodeAudioData,AudioBufferSourceNode):- Decoding incoming audio chunks.
- Queueing and playing audio seamlessly.
- Minimizing gaps for a natural listening experience.
- WebSocket
onmessagehandler: Processing different types of messages (transcription, final response text, audio chunks).
4. Backend: Flask, WebSockets, and OpenAI Integration
This section will detail the Python Flask server.
4.1 Setting up the Flask Application
- Installation:
pip install Flask Flask-SocketIO openai python-dotenv - Basic Flask app structure.
4.2 Handling WebSockets with Flask-SocketIO
Flask-SocketIO: For bi-directional, real-time communication.@socketio.on('connect'),@socketio.on('disconnect'),@socketio.on('message'): Event handlers.- Receiving audio chunks: Processing incoming base64 audio.
4.3 Integrating OpenAI APIs
- Authentication: Setting
OPENAI_API_KEYenvironment variable. - Whisper API (Speech-to-Text):
- Receiving audio chunks.
- Accumulating audio and sending to Whisper. (For real-time, we’d ideally send smaller chunks or use an async Whisper stream if available or process VAD-detected segments). For simplicity, we’ll accumulate a bit and then send.
openai.audio.transcriptions.create(file=..., model="whisper-1")
- Chat Completions API (GPT):
- Maintaining conversation history.
- Sending transcription to GPT.
- Streaming responses for low latency.
openai.chat.completions.create(model="gpt-4o", messages=..., stream=True)
- Text-to-Speech API (TTS):
- Receiving streamed text chunks from GPT.
- Sending text chunks to TTS API.
- Streaming audio back to the frontend.
openai.audio.speech.create(model="tts-1", voice="alloy", input=..., response_format="opus")
# app.py
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, jsonify
from flask_socketio import SocketIO, emit
import openai
import base64
import io
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# Load environment variables from .env file
load_dotenv()
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = os.getenv('SECRET_KEY', 'your_secret_key_here') # Use a strong secret key
socketio = SocketIO(app, cors_allowed_origins="*")
openai.api_key = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY')
# Store conversation history for each client
client_conversations = {}
# --- Helper Functions for OpenAI Interactions ---
async def transcribe_audio_chunk(audio_bytes):
"""Transcribes a raw audio chunk using OpenAI Whisper."""
try:
# OpenAI expects a file-like object
audio_file = io.BytesIO(audio_bytes)
audio_file.name = "audio.webm" # Whisper needs a filename and format hint
# Consider using a more advanced streaming ASR if latency is critical
# For simplicity, we're sending accumulated chunks.
response = openai.audio.transcriptions.create(
model="whisper-1",
file=audio_file,
response_format="json"
)
return response.text
except openai.APIError as e:
app.logger.error(f"OpenAI Whisper API error: {e}")
return None
async def get_gpt_response_stream(session_id, user_message_text):
"""Gets a streaming response from OpenAI GPT."""
if session_id not in client_conversations:
client_conversations[session_id] = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful AI assistant. Respond concisely but completely."}
]
client_conversations[session_id].append({"role": "user", "content": user_message_text})
try:
stream = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o", # Using gpt-4o for its multimodal capabilities and speed
messages=client_conversations[session_id],
stream=True,
)
full_assistant_response = ""
for chunk in stream:
content = chunk.choices[0].delta.content
if content:
full_assistant_response += content
# Emit partial text responses to the frontend for display
socketio.emit('message', {'type': 'response_text', 'text': content}, room=session_id)
yield content # Yield chunks for TTS
# Add the full assistant response to the conversation history
client_conversations[session_id].append({"role": "assistant", "content": full_assistant_response})
except openai.APIError as e:
app.logger.error(f"OpenAI GPT API error: {e}")
yield "An error occurred while getting a response." # Yield error message
async def stream_text_to_speech(text_chunks, session_id):
"""Streams text chunks to OpenAI TTS and sends audio back to client."""
full_text_for_tts = "".join(text_chunks) # Join chunks for a more coherent TTS call
try:
# OpenAI TTS API now supports streaming audio back
with openai.audio.speech.create(
model="tts-1",
voice="alloy", # You can choose other voices like 'nova', 'shimmer', 'fable', 'onyx', 'echo'
input=full_text_for_tts,
response_format="opus", # opus is good for browser and streaming
) as response:
for chunk in response.iter_bytes(chunk_size=4096): # Adjust chunk size as needed
# Encode audio chunk to base64 for WebSocket transmission
base64_audio = base64.b64encode(chunk).decode('utf-8')
socketio.emit('message', {'type': 'audio_chunk', 'audio_base64': base64_audio}, room=session_id)
except openai.APIError as e:
app.logger.error(f"OpenAI TTS API error: {e}")
error_speech = await stream_text_to_speech(["I'm sorry, I couldn't generate speech."], session_id)
# --- Flask Routes ---
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
# --- SocketIO Event Handlers ---
@socketio.on('connect')
def handle_connect():
session_id = request.sid
client_conversations[session_id] = [] # Initialize conversation for new client
app.logger.info(f"Client connected: {session_id}")
emit('message', {'type': 'response_text', 'text': 'Hello! How can I help you today?'}, room=session_id)
@socketio.on('disconnect')
def handle_disconnect():
session_id = request.sid
if session_id in client_conversations:
del client_conversations[session_id] # Clean up conversation history
app.logger.info(f"Client disconnected: {session_id}")
@socketio.on('message')
async def handle_message(data):
session_id = request.sid
if data['type'] == 'audio':
audio_base64 = data['audio_base64']
audio_bytes = base64.b64decode(audio_base64)
# Transcribe audio
transcription = await transcribe_audio_chunk(audio_bytes)
if transcription:
app.logger.info(f"Transcription: {transcription}")
emit('message', {'type': 'transcription', 'text': transcription}, room=session_id)
# Get GPT response (streaming)
gpt_response_chunks = []
async for chunk in get_gpt_response_stream(session_id, transcription):
gpt_response_chunks.append(chunk)
# Stream TTS audio back to client
await stream_text_to_speech(gpt_response_chunks, session_id)
else:
emit('message', {'type': 'response_text', 'text': 'Sorry, I could not understand your audio.'}, room=session_id)
else:
app.logger.warning(f"Unknown message type: {data['type']}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Ensure OPENAI_API_KEY is set
if not openai.api_key:
raise ValueError("OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable not set. Please set it in your .env file or environment.")
# Run with reloader for development (remove in production)
socketio.run(app, debug=True, allow_unsafe_werkzeug=True) # allow_unsafe_werkzeug=True for non-prod SSL cert warningsTo run this code:
- Save the HTML content as
templates/index.html. - Save the Python content as
app.py. - Create a
.envfile in the same directory asapp.pyand add your OpenAI API key:OPENAI_API_KEY="YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY_HERE" SECRET_KEY="A_VERY_STRONG_RANDOM_SECRET_KEY" - Install dependencies:
pip install Flask Flask-SocketIO openai python-dotenv5. Run the Flask app:
python app.py 6. Open your browser to http://localhost:5000.
5. Enhancements and Advanced Considerations
- Voice Activity Detection (VAD):
- Implementing VAD to detect when a user starts and stops speaking.
- This allows for more intelligent chunking of audio for Whisper and prevents sending silence. (e.g.,
webrtcvadin Python).
- Error Handling and Robustness:
- Graceful handling of API failures, network issues, and microphone access errors.
- Retries and fallback mechanisms.
- Latency Optimization:
- Aggressive audio chunking for Whisper (if Whisper supports true streaming, otherwise using VAD for smaller, faster segments).
- Streaming text from GPT before the full response is ready.
- Streaming audio from TTS.
- Choosing optimal audio codecs (Opus is excellent).
- Context Management:
- More sophisticated conversation history management (e.g., summarizing old turns to stay within token limits).
- Personalization based on user preferences.
- User Interface (UI) Feedback:
- Visual indicators for listening, processing, and speaking states.
- Displaying partial transcriptions.
- Deployment:
- Securing WebSockets (WSS/SSL).
- Scaling the Flask application (e.g., Gunicorn, Nginx, cloud platforms).
- Rate limiting API calls.
6. Challenges and Limitations
- API Costs: OpenAI API usage incurs costs, especially with extensive audio and GPT processing.
- Latency vs. Accuracy: Balancing the need for real-time response with the accuracy of ASR and LLM output.
- Offline Capabilities: The current setup relies heavily on cloud APIs; true offline operation is not feasible.
- “Hallucinations” and Bias: LLM inherent limitations.
- Privacy: Handling user audio data and conversation history.
7. Conclusion: The Future is Conversational
- Recap of what we built and learned.
- The immense potential of real-time voice AI.
- Future directions: Multimodality, deeper integration, personalized AI assistants.
- Encouragement to experiment and build further.

Comments